
The ubiquity of electronic devices and the internet makes this a convenient resource for the current generation of learners.
CALCULATION OF BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS SERIES
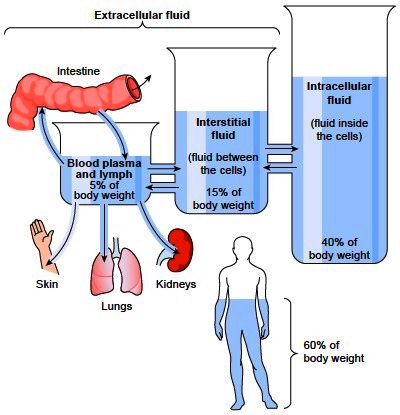
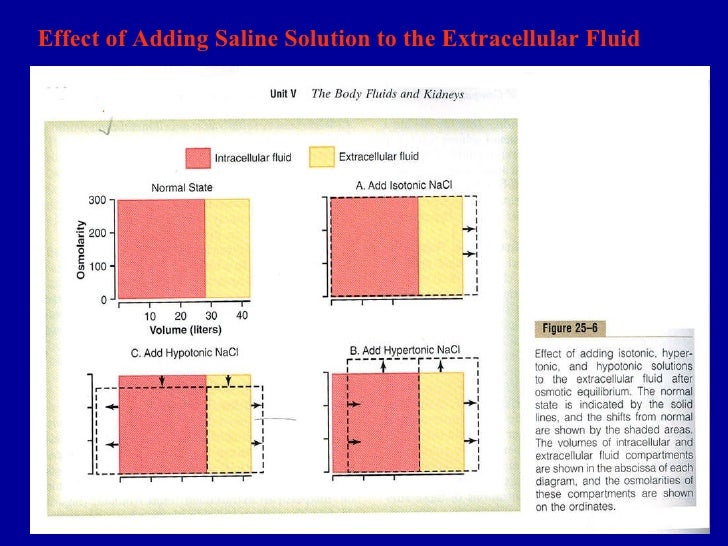
The purpose/goal of this resource is to help the student learn clinically relevant physiology using a series of short video-blackboard tutorials that cover body fluid compartments and the regulation of both extracellular fluid volume (NaCl) and body osmolality (water). All students in this course met the course learning objectives, performed well on the final examination, and passed the course. When used as a flipped classroom elective for fourth-year medical students, the videos were well utilized and highly rated by students. Compared to a historical control year, the addition of our video tutorials to the renal physiology course resulted in an 11-point increase in performance on the renal section multiple-choice questions. When used with first-year medical students, 59% said these videos were a more helpful resource compared to live lectures and course notes. For the fourth-year medical student course, the videos were required viewing prior to classroom sessions that involved case discussions and problem solving. This module relies heavily on diagrams, cartoons, and graphs to meet the learning objectives. These specific videos cover body fluid compartments and the regulation of both extracellular fluid volume (NaCl) and body osmolality (water). In response, the instructors created videos to serve as a learning resource for a first-year medical student course in normal body physiology, and for a fourth-year flipped-classroom elective on IV fluids and electrolyte disorders. M U is usually calculated from C U, the concentration of marker lost in the urine and V U, the volume of the urine thus: M U C U. Studies have been performed analyzing the characteristics and best practices for instructor-led videos. Where V is the volume of the body fluid compartment, M is the mass of marker injected, M U is the mass of marker lost in the urine during equilibration and C is the measured concentration of the marker.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
